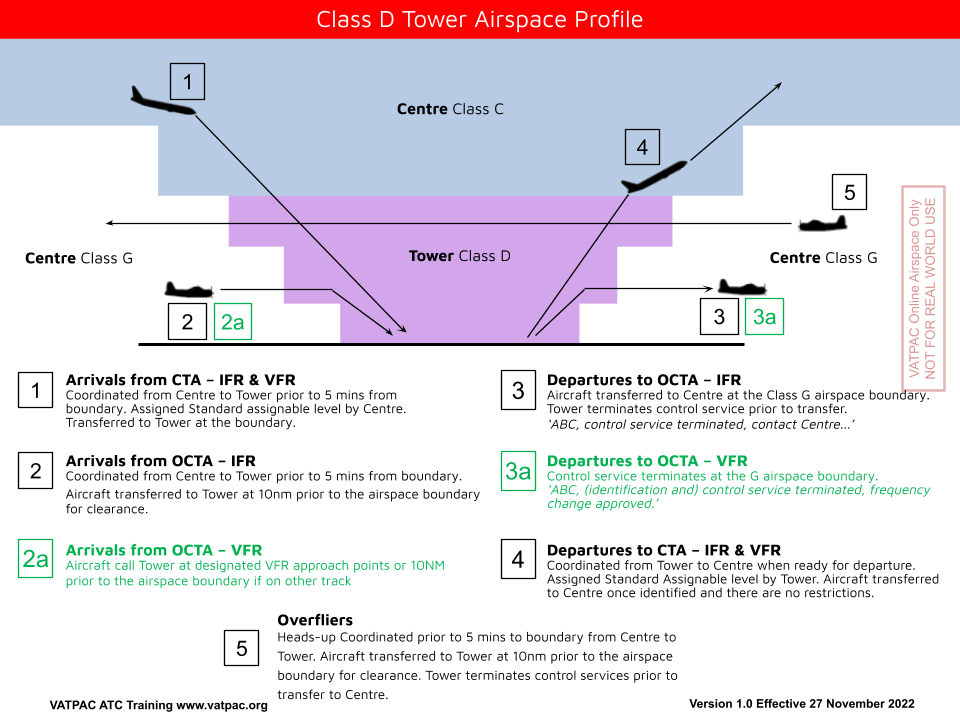
Class D Tower
Airspace
Remember that in Class D Airspace, IFR aircraft are separated from IFR and SVFR, and SVFR is separated from SVFR when visibility is not VMC. No separation is provided for VFR aircraft, even though it is controlled airspace. The Tower Controller provides more of a "Segregation" service (ie, providing reasonable opportunity for the aircraft to separate themselves), as well as providing traffic information.
Surveillance
Although Surveillance standards cannot be used for separation at Class D Towers, overlying TCU/Enroute controllers can use their surveillance standards to help Class D towers achieve separation, when procedural separation is a bit awkward or impractical.
Phraseology
AY ADC -> BLA: "Can you advise when QLK208D is 5nm clear of DSB?"
BLA -> AY ADC: "Affirm, will do"
...
BLA -> AY ADC: "QLK208D, 5nm clear of DSB"
AY ADC -> BLA: "QLK208D, 5nm clear of DSB, thanks"
Lateral
45° Segregated Flight Paths
Straight-in
- Can be applied between departures and arrivals when the departing aircraft's flight path and the arrival aircraft's flight path are at least 45° clear of each other, and, for a straight-in approach, the arriving aircraft is at least 5nm from the arrival runway threshold
Visual, DME/GNSS, Circle to land
- Can be applied between departures and arrivals when the departing aircraft's flight path and the arrival aircraft's flight path are at least 45° clear of each other, and, for a Visual, DME/GNSS or Circle to land approach, the arriving aircraft is at least 10nm from the airfield
Vertical
1000ft
- Between any aircraft